Cell Genetics
Research Focus
General Facts
Research
Selected Publications
Selected Funding, Collaboration
Keywords: T-lymphocyte signalling, T-cell effector/memory functions, autoimmunity, cancer immunity, innovative immunotherapy concepts.
Research (ÖSTAT Classification) : 301902, 302055, 301303
Research Focus
The cell genetics team has expertise in mouse genetics and in signal transduction analyses of effector/memory T-cell differentiation and the ability of these cells to alter adaptive immune response outcomes. In particular, we have acquired experience in the investigation of molecular signalling processes through the use of hypothesis-driven mechanistic studies and by using unbiased CRISPR/Cas9-based genetics screens and RNA sequencing to characterise key protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions.
General Facts
In order to understand the physiology and pathophysiology of T-lymphocyte biology, it is necessary to decode the biochemical processes that integrate key signals received from antigen, cytokine and integrin-receptors as well as inhibitory receptors. The underlying goal of our work is to understand the selective functions of defined signal transduction pathways in CD4+ and CD8+ T-lymphocytes and to use this information to develop strategies for manipulating the immune response, either in order to promote immunosuppression in the context of autoimmune diseases and graft rejection or for augmentation as part of an innovative cancer immunotherapy-based approach.
In the exploration of distinct members of the AGC family of protein serine/threonine kinases and their effector substrates, our recent data strongly suggest that T-cell-based immunotherapies could benefit greatly from the modulation of key signalling pathways that govern T-cell dysfunctions, i.e. in cancer-mediated immune evasion. Remarkably, the strategy of intracellular NR2F6 and/or Cbl-b checkpoint-targeting therefore appears to be particularly capable of improving efficacy and broadening the applicability of cancer immunotherapy regimes and it consequently has the potential to lead to prolonged patient survival in the future.
Research
Cell Genetics Team Research Focus:
Gottfried Baier, Nikolaus Thuille, Victoria Klepsch, Natascha Kleiter, Thomas Gruber, Kerstin Bellaire-Siegmund, Karin Albrecht-Schgör, Bojana Jakic, Sebastian Peer, Will Olson, Friedrich Fresser, Nina Posch, Maria Pommermayr, Tajana Sajinovic, Dominik Humer et al.
Mechanistic Understanding of T-Cell Persistence in Host-Protective Tumour Immunity
The Cell Genetics team was the first to reveal the T-lymphocyte-intrinsic PKCtheta/NR2F6/Cbl-b axis as an essential signalling node governing the complex host-tumour interactions at the intersection between inflammation and cancer. Modulation of this signalling pathway renders effector T-cells capable of rejecting otherwise lethal tumour burdens and their metastases in preclinical cancer model systems. Our research aims to elucidate the inter and intra-cellular mechanisms that reshape the immune contexture to allow superior tumour rejection (Fig. 1).
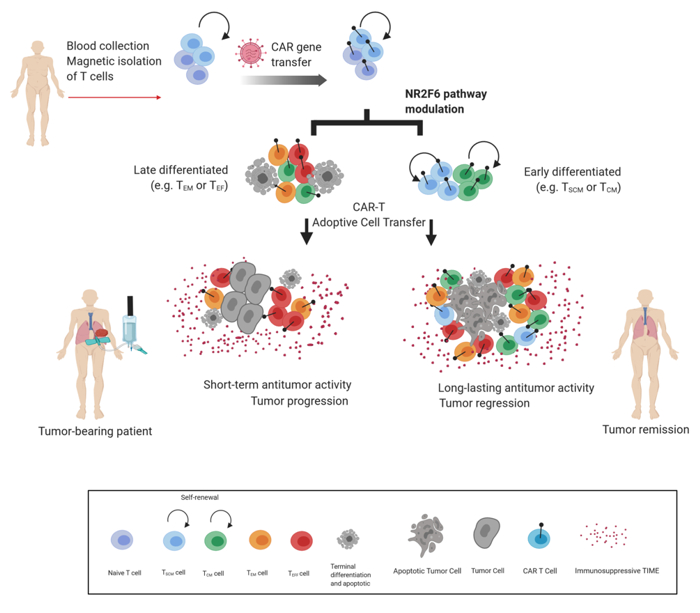
Fig. 1: Leverage of CD8+ T-cell persistence to extend Chimeric Antigen T cell-engineered (CAR-T) therapy to solid cancer.
Role of NR2F6 in Autoimmunity
Natascha Kleiter
Adaptive immune responses are tightly regulated, in order to avoid self-recognition that could lead to autoimmune disease. The orphan nuclear receptor NR2F6 is a validated key player in the suppressor pathway of T-cell-mediated immunity. The research employs biochemical, molecular and cellular analyses of the signal transducing nuclear receptor network of NR2F6 within the CD4+ T-cell subsets that orchestrate humoral immune responses (Fig. 2).
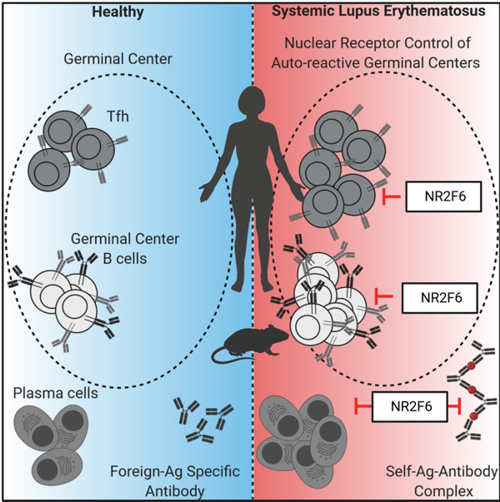
Figure 2: Role of NR2F6 and its implications for autoimmune disease.
Role of E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Cbl-b in Cancer Immunity
Thomas Gruber
Adoptive transfer with genetically silenced Cbl-b CD8+ T-lymphocytes significantly enhances anti-tumour effects in immune-competent recipient mice. The purpose of the translational research collaboration is to elucidate the underlying mechanisms in immune cells, by means of which the Cbl-b pathway attenuates their effector responses in an immunosuppressive tumour environment (Fig. 3).

Fig. 3: Image of a cytotoxic CD8+ T-lymphocyte employed in the study.
Sox Matters!(FWF 1000 ideas programme)
Kerstin Bellaire-Siegmund
It is suspected that T-cell-intrinsic factors govern the sex disparity seen in cancer immunity. By focusing on the involvement of key molecular pathway switches, this project aims to validate the x-linked transcription factor Sox3 as a novel cancer immune checkpoint candidate involved in the sex dimorphism of the adaptive immune system. In particular, the study focuses on the mechanistic characterisation of Sox3 and its pathway signature(s) in the immune evasion of cancer.
Selected A2aR Blockade as Treatment for CM (FWF 1000 ideas programme)
Karin Albrecht-Schgör
Cerebral malaria (CM) represents an immune mediated disease in which CD8+ T-lymphocytes play a key role in the pathophysiology. By employing both genetic and pharmacological adenosine A2a receptor (A2aR) pathway inhibition approaches, this project aims to validate the causal role of lymphatic A2aR in an experimental mouse model of CM. This will make it possible to decipher mechanistic knowledge during CM disease progression, thus paving the way for immunotherapy regimes in the future.
Selected Publications
- Jayachandran, Rajesh; Gumienny, Aleksandra; Bolinger, Beatrice; Ruehl, Sebastian; Lang, Mathias Jakob; Fucile, Geoffrey; Mazumder, Saumyabrata; Tchang, Vincent; Woischnig, Anne-Kathrin; Stiess, Michael; Kun, Gabriele; Claudi, Beatrice; Schmaler, Mathias; Siegmund, Kerstin; Li, Jianping; Dertschnig, Simone; Hollaender, George; Medina, Eva; Karrer, Urs; Moshous, Despina; Bumann, Dirk; Khanna, Nina; Rossi, Simona W.; Pieters, Jean: Disruption of Coronin 1 Signalling in T-Cells Promotes Allograft Tolerance while Maintaining Anti-Pathogen Immunity. IMMUNITY 2019; 50(1); 152 doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.12.011
- Meryk, A.; Pangrazzi, L.; Hagen, M.; Hatzmann, F.; Jenewein, B.; Jakic, B.; Hermann-Kleiter, N.; Baier, G.; Jylhävä, J.; Hurme, M.; Trieb, K.; Grubeck-Loebenstein, B.: Fc mu receptor as a Costimulatory Molecule for T-Cells.
CELL REPORTS. 2019; 26(10); 2681-2691.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.02.024 - Olson, William J.; Jakic, Bojana; Labi, Verena; Schoeler, Katia; Kind, Michaela; Klepsch, Victoria; Baier, Gottfried; Hermann-Kleiter, Natascha: Orphan Nuclear Receptor NR2F6 Suppresses T Follicular Helper Cell Accumulation through Regulation of IL-21.
CELL REPORTS. 2019; 28(11); 2878-+. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.08.024 - Siegmund, Kerstin; Thuille, Nikolaus; Posch, Nina; Fresser, Friedrich; Leitges, Michael; Baier, Gottfried: Novel mutant mouse line emphasizes the importance of PKCtheta for CD4+ T-lymphocyte activation.
CELL COMMUNICATION AND SIGNALING. 2019; 17(S); 56. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0364-0 - Thuille, Nikolaus; Siegmund, Kerstin; Klepsch, Victoria; Schoergenhuber, Jacqueline; Danklmaier, Sarah; Leitges, Michael; Baier, Gottfried: Loss-of-function phenotype of a PKCtheta(T219A) knockin mouse strain.
CELL COMMUNICATION AND SIGNALING. 2019; 17(1); 141. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0466-8
Patents
- (WO/2008/117327) ASSAY METHOD FOR IDENTIFYING PKCtheta INHIBITORS
- (WO/2009/073905) METHOD FOR INCREASING IMMUNOREACTIVITY
- (WO/2010/004052) AGONISTS OF NR2F6 FOR IMMUNOSUPPRESSION
- (WO/2010/004051) NR2F6 ANTAGONISTS FOR AUGMENTING CANCER IMMUNITY
- (WO/2011/119061) METHOD FOR DETERMINING Cbl-b EXPRESSION
Selection of Funding
- PhD program in Molecular Cell Biology and Oncology, Austrian Science Funds (FWF) DK-MCBO, ZFW011010-18 (Natascha Kleiter)
- NR2F6 steuert Immunreaktionen bei Infektionen, Austrian Science Funds (FWF) P28694 (Natascha Kleiter)
- The TGFβ/Cbl-b pathway in autoimmunity and tumour immunity, Austrian Science Funds (FWF) P26892 (Thomas Gruber)
- Sox macht den Unterschied), Austrian Science Funds (FWF), 1000 Ideen Programm TAI 88 (Kerstin Siegmund-Bellaire)
- Therapie zerebraler Malaria mit Adenosin 2a Rezeptor Blockade, Austrian Science Funds (FWF), 1000 Ideen Programm TAI 80 (Karin Albrecht-Schgör)
- PhD program in Molecular Cell Biology and Oncology, Austrian Science Funds (FWF) DK-MCBO, ZFW011010-05 (Gottfried Baier)
- Immunoregulatory role of A2aR, Austrian Science Funds (FWF) P30324 (Gottfried Baier)
- CD Laboratory for cancer immune therapy; Acronym: I-CARE (1.FP), Christian Doppler Society (CDG) (Gottfried Baier)
- Human relevance of NR2F6 as lymphatic biomarker, Austrian Central Bank, OeNB #17551 (Gottfried Baier)
- NR2F6 as bona-fide cancer immune checkpoint, Austrian Science Funds (FWF) P31383 (Gottfried Baier)
- ERC-ADV HOPE: Host Protective Engineering of Cancer Immunity, EC Horizon 2020 #786462 (Gottfried Baier)
Collaborations
- Jürgen Wagner and Gerhard Zencke; Novartis Pharma, Basel, Switzerland
- Noah Isakov, Ben Gurion University of the Negev, Israel
- Wallace Langdon, University of Western Australia, Perth, AUS
- Arthur Kaser, Department of Gastroenterology, Cambridge, UK
- Shoji Yamamoto, Daiichi Sankyo Ltd., Tokyo, Japan
- Michael Leitges, Memorial University of Newfoundland, St. John`s, Canada
 Univ.-Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Gottfried Baier
Univ.-Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Gottfried Baier
Director
Contact:
Peter Mayr Straße 1a
6020 Innsbruck
Austria
Email: Gottfried.Baier@i-med.ac.at
Phone: +43 512 9003 705 14
Fax: +43 512 9003 73518
www.baierlab.com



